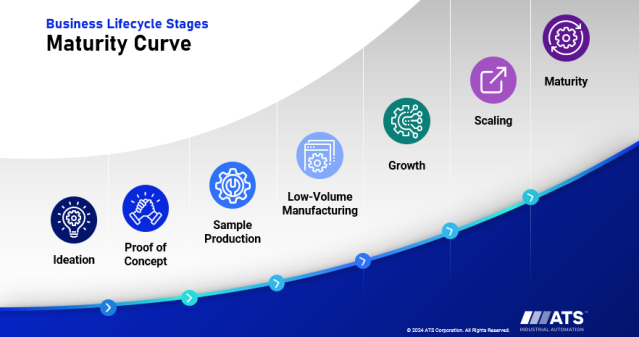
As manufacturing environments grow more complex, the need for effective, scalable training has never been greater. Traditional methods like classroom instruction, job shadowing, and static videos are no longer sufficient to prepare workers for high-risk, high-precision tasks.
In episode 59 of Digitalization Tech Talks, ATS Industrial Automation experts explore how virtual reality (VR) helps manufacturers overcome today’s training challenges, build a more capable workforce, and unlock smarter maintenance and performance tracking.
Read on for highlights from the episode, then tune in to hear the full conversation.
The Training Gap in Modern Manufacturing
Manufacturers face many obstacles when it comes to onboarding and upskilling workers, from safety risks to knowledge gaps. High turnover rates mean manufacturing companies are constantly training new employees, often without standardized processes across departments or sites.
Skilled trainers are also often in short supply, and production demands limit the time available for hands-on instruction. In many cases, training on live equipment is either disruptive to workflows, poses safety concerns or is outright impossible.
Safety and compliance requirements add another layer of complexity. In high-risk environments such as nuclear facilities or chemical plants, access to equipment for training may be restricted due to the high risks involved. These limitations make it difficult to ensure workers are adequately prepared before stepping into real-world situations.
Why Traditional Methods Aren’t Enough
Conventional training formats often fail to replicate the pressures and complexity of real manufacturing environments. Passive learning techniques, like watching videos or attending lectures, don’t engage learners or help them retain critical information. Additionally, these methods are often one-size-fits-all, ignoring the diverse learning styles and skill levels of each employee.
Time constraints faced by most manufacturers regardless of industry, and information overload further reduce the effectiveness of traditional training. Workers are expected to understand large amounts of material quickly, which can lead to gaps in understanding. What’s more, these methods struggle to keep pace with the rapid evolution of manufacturing technologies.
The VR Advantage: Immersive and Safe
By simulating real-world tasks in a controlled environment, VR enables hands-on learning without the risks associated with physical equipment. Learners can repeat procedures to build confidence and master complex skills at their own pace.
One of VR training’s most impactful features is gamification. Training modules are structured like levels in a game — starting with guided instructions and visual cues, then gradually removing assistance as learners progress. This approach fosters deeper engagement and helps employees develop problem-solving skills, while motivating them to keep learning.
VR training is also particularly valuable in high-risk industries. Immersive simulations allow workers to rehearse critical maintenance tasks—such as accessing reactor vaults or performing heavy lifts—without exposure to radiation or other hazards. These scenarios can be repeated as often as needed, ensuring safety and compliance.
How Manufacturers are Using VR
Virtual reality training is being harnessed across various manufacturing applications. Operator training is a major area of focus, especially for tasks like material replenishment, product changeovers, and routine maintenance. These activities keep production lines running smoothly and can significantly reduce downtime.
Standardized VR modules for specific machines also enable manufacturers to scale training efforts. Once developed, these modules can be deployed across multiple customer sites, making VR a cost-effective solution for manufacturers and consumers.
Measuring Success: Data and Analytics in VR Training
Beyond its immersive capabilities, virtual reality provides valuable data that helps manufacturing teams track training effectiveness.
One of VR’s biggest advantages is its ability to generate actionable data such as missteps, hesitation points, and common errors. It can also identify key gaps in training and improve content for greater learning effectiveness.
This data is also useful for informing process improvements. For example, VR can simulate lean management scenarios, allowing teams to test and optimize modifications in a virtual environment before implementing them on the shop floor.
VR isn’t just a training tool—it’s a performance analytics engine that helps organizations improve operations, scale, and become more competitive.
Getting Started: How to Deploy VR Training
Adopting virtual reality training doesn’t require a massive overhaul. The most successful implementations begin with a single high-impact use case and a flexible mindset.
Not every learner may be comfortable with a VR headset, so platforms that support multiple formats, including desktop interfaces, are becoming popular. By collaborating with an experienced automation partner like ATS, manufacturing leaders can align technologies with business needs, build momentum, and drive higher performance across their organizations.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Immersive Tech
The evolution of immersive technology is just beginning. Augmented reality (AR) is poised to enhance employee training by overlaying real-time data into the operator’s field of view. Spatial computing will enable gesture-based interaction with virtual environments, making training even more intuitive and responsive. Connected worker platforms will also link digital work instructions with live operational data.
These advancements will make immersive technologies an integral part of smart manufacturing, supporting continuous learning and real-time decision-making.
FAQ: Your Top VR Training Questions Answered
Q1: How does VR improve safety and compliance training?
Virtual reality allows workers to practice critical tasks in a safe, controlled environment, especially in industries like nuclear, where hands-on training can pose major risks.
Q2: What use cases benefit most from VR?
VR is ideal for equipment maintenance, assembly procedures, safety protocols, and operator training across industries.
Q3: What kind of analytics does VR provide?
Data on missteps, hesitation, and performance trends—helping organizations improve training, workflows, and processes.
Q4: What are the adoption challenges?
Cost, integration, and cultural resistance. These can be overcome by starting small, demonstrating returns on investment (ROI), and choosing flexible platforms.
Q5: What’s next for immersive tech?
Augmented Reality (AR), spatial computing, and connected worker platforms will make training more intuitive, data-driven, and integrated with operations.
Listen Now
Ready to hear the full conversation? Tune in to episode 59 of Digitalization Tech Talks and discover how ATS Industrial Automation and Siemens are shaping the future of manufacturing training.
Key Takeaways from Episode 59
- VR training helps manufacturers overcome traditional barriers like trainer shortages, safety risks, and poor retention.
- Deployment is scalable and flexible, with measurable ROI and performance improvements.
- Siemens software enhances VR capabilities, enabling smarter maintenance and operational efficiency.
Every project is unique. Allow us to listen to your challenges and share how automation can launch your project on time.

Ian Menzies
Vice President, Technology
ATS Industrial Automation
Ian leverages 17+ years of experience to lead high-profile design projects from feasibility to commissioning. His technical expertise in asset management and technical due diligence ensures optimal solutions for customers, enhancing their operational efficiency and success.