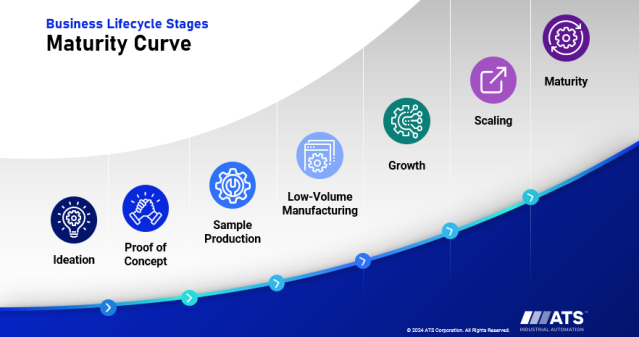
It’s a buzzword that’s mentioned in almost every manufacturing conversation, but how exactly does digitalization technology work?
Digitalization technology transforms physical processes into digital ones, enabling manufacturers to leverage real-time data collection, analysis, and optimization. Plant managers and line managers can monitor performance, predict maintenance needs, and improve efficiency by creating digital twins of physical assets. This technology leverages Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning (ML) to streamline operations.
Digitalization optimizes assembly lines by integrating IoT devices and sensors to collect real-time data, which can then be analyzed using AI/ML algorithms. This data-driven approach helps operators identify bottlenecks, predict maintenance needs, and improve overall efficiency. Finally, digitalization enables a more engaging, safe employee training environment by providing simulations of assembly lines, allowing workers to practice and understand important manufacturing processes risk-free.
Simulation
Simulation in manufacturing involves creating a virtual model of a production process or system. This model tests and analyzes different scenarios, such as production schedule changes, equipment configurations, or process parameters. Teams can also digitalize entire lines before they’re built in the real world. By simulating these scenarios, manufacturers can predict outcomes, identify potential issues, and optimize processes before implementing them on the floor. This reduces the risk of costly errors and improves overall efficiency.
Virtual Commissioning
Virtual commissioning is the process of using digital models to test and validate the performance of new equipment or systems before they’re physically installed. This involves creating a virtual replica of the production line and running simulations to ensure the new equipment integrates seamlessly with existing systems. Virtual commissioning helps teams identify and resolve potential issues, reducing downtime and ensuring a smooth transition while installing new equipment.
System Twin
System twins are advanced virtual representations of entire manufacturing systems. They provide a comprehensive digital model that mimics the physical attributes and behaviors of machines, robots, software, and other components integrated within a manufacturing line. System twins also enable remote monitoring and diagnostics of machines so experts can diagnose and potentially resolve issues, even if they’re not physically present.
Digital Shadow
Digital Shadows utilize digital replicas (System Twins) of entire manufacturing systems, including all machines, devices, and processes. IoT devices and sensors connect these virtual models to their physical counterparts, allowing for real-time data exchange. Digital Shadow enables manufacturers to monitor, analyze, and optimize the performance of their entire production line, predict maintenance needs, and simulate changes to improve productivity.
Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance leverages digital technologies such as IoT, AI, and ML to predict and prevent equipment failures. By continuously monitoring the condition of machinery and analyzing the data in real time, smart maintenance systems can identify potential issues before they lead to costly, unexpected breakdowns. This proactive approach reduces downtime, extends the lifespan of equipment, and improves operational efficiency.
Advanced Employee Training
Virtual reality (VR) training uses immersive simulations to give employees a realistic and interactive learning experience. VR training allows workers to practice complex tasks, understand production processes, and develop skills in a controlled environment. VR training improves learning retention, reduces training costs, and enables training employees for scenarios that would otherwise be difficult or dangerous to learn in the real world.
Benefits of Digitalization Technology
Digitalization is an essential component for modern industrial operations, offering numerous advantages that significantly enhance ongoing processes, including:
- Efficiency and Productivity: Digitalization integrates IoT devices and sensors to collect concurrent data. This data is analyzed using AI and machine learning algorithms to identify bottlenecks and optimize workflows.
- Cost Reduction: Manufacturers can reduce expenses through digitalization. Real-time data collection and analysis enable teams to better manage resources, minimize waste, and improve energy outputs. Meanwhile, preventive maintenance can help prevent costly equipment failures and extend the lifespan of machinery.
- Improved Quality: Digitalization ensures better quality control by providing precise, accurate data for monitoring and evaluation. Advanced algorithms and AI can quickly detect anomalies and errors, allowing for immediate corrective actions. This reduces the likelihood of defects and ensures consistent product quality, ultimately leading to higher customer satisfaction.
Challenges and Considerations
When implementing digitalization in manufacturing, manufacturing leaders must keep several considerations in mind:
- Integration with Existing Systems: Adding digitalization technology to legacy systems can present significant challenges. Many existing systems weren’t designed to communicate with modern digital technologies, leading to compatibility issues. Integration requires careful planning, including the use of middleware solutions, application programming interfaces (APIs), and custom interfaces for seamless data exchange. Moreover, the process can be technically challenging, as it may involve upgrading or replacing outdated equipment and software.
- Skill Requirements: Successful implementation and operation of digitalization technology demands skilled professionals proficient in IoT, AI/ML, and data analytics from an automation partner. These digital experts can design, deploy, and maintain digital systems. What’s more, they can interpret and act on the collected data, and they have the knowledge and experience to apply it within a manufacturing environment.
- Data Security and Privacy: Manufacturers that embrace digitalization must secure digital data and maintain privacy. As teams collect more data through IoT devices and sensors, the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches becomes a concern. Robust cybersecurity measures such as encryption, secure access controls, and regular security audits help protect sensitive or confidential business information.
Digitalization technology has the potential to transform industries by converting physical processes into digital ones, enabling real-time data collection, analysis, and optimization. This technology leverages IoT, AI, and machine learning to drive problem-solving and streamline operations. Digitalization empowers manufacturers to remain competitive while saving critical resources, from leveraging digital twins of physical assets to predicting maintenance needs. The benefits of digitalization extend beyond operational efficiency, offering improved quality control and better-informed decision making. Embrace the future by exploring and adopting digitalization for manufacturing to unlock new opportunities for growth.
Every project is unique. Allow us to listen to your challenges and share how automation can launch your project on time.

Roland Echter
General Manager - Digital
ATS Industrial Automation
Roland has helped companies across numerous industries to automate and optimize production with digital solutions. Roland works with customers to configure services, systems, using digital tool strategies to build and scale production and drive operational efficiency.