Warranty recalls and penalties can be a significant financial burden for manufacturers. On average, warranty costs account for about 1.5% of a company’s revenue in the manufacturing sector. However, this percentage can vary widely depending on the industry and company. For instance, some automotive companies have warranty costs as high as 4.5% of their revenue.
Product recalls due to safety issues or defects can lead to substantial legal expenses and damage a company’s reputation. The financial impact of these recalls isn’t limited to direct costs but also includes lost sales, decreased consumer trust, and sometimes liability. How can companies reduce this risk?
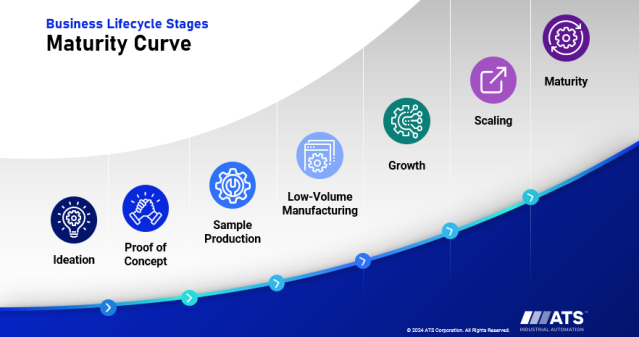
The Value of Assembly Line Testing
Comprehensive testing throughout the assembly line as a product is being manufactured is essential to maintaining high-quality standards and minimizing the financial and reputational risks associated with product recalls. In-line testing ensures each product part and value-added step in the process meets the required standards before moving farther down the line. In this way, companies can also minimize the risk of scrapping a batch of the product later in the manufacturing process. Detecting and correcting component issues early saves critical time and resources — especially for startups—allowing them to optimize assembly costs and efficiently scale up to full production.
Moreover, in-line testing significantly reduces the likelihood of product recalls. By catching issues early, companies can prevent faulty products from reaching consumers, avoiding substantial legal costs and damaging their reputation. This proactive approach ensures product quality and helps maintain consumer trust, two crucial elements when it comes to battery production.
Line Testing Considerations
Manufacturers must consider several elements when determining testing in an assembly line. The appropriate testing approach will depend on the specific processes and products involved. Manufacturers must evaluate factors such as the complexity of the product, the criticality of its components, and the potential impact of defects on overall performance. The testing strategy must also align with industry and regulatory requirements to ensure compliance.
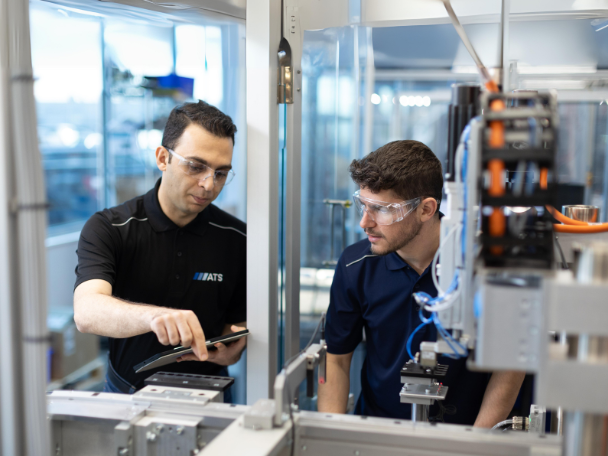
Teams can implement various tests to ensure comprehensive validation. In-process testing is essential to catch problems early in production, reducing scrap, minimizing rework, and maximizing overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). End-of-line testing serves as the final checkpoint to ensure the product is commercially viable before reaching consumers. Leak testing, electrical testing, and functional testing are all standard methods used to verify the quality of different aspects of the product.
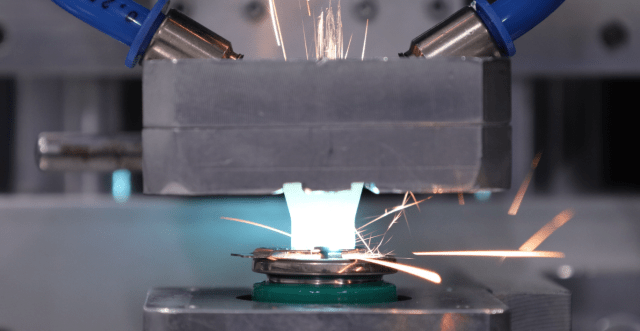
Testing is particularly important in validating welding processes, especially when weld quality directly impacts product reliability. For instance, robust laser welding processes are critical to electric vehicle (EV) battery pack assembly. Each weld site must be thoroughly tested to ensure a high success rate, as bad welds can significantly affect battery performance. Real-time monitoring and automated clamping solutions can ensure precise, strong welds, validating each step of the welding process while ensuring the quality of the finished pack.
Leak Testing
Leak testing is essential to make sure products, especially those with electrical components, are properly protected from liquid. This helps prevent damage and reinforces safety by detecting any potential leaks that could compromise the product’s integrity. This type of testing helps maintain quality by ensuring all components are sealed correctly, which is particularly important for products exposed to rain, snow, salt, or sand. Leak testing also helps avoid costly recalls and warranty claims by catching defects quickly during production.
Key considerations for this approach include the type of product being tested and the specific requirements for leak detection. For instance, products with electrical components must be tested to ensure they meet Ingress Protection (IP) ratings, which indicate the level of protection against liquids entering the product. The testing environment must also be controlled to account for temperature changes or environmental factors that could affect the accuracy of the test. Furthermore, the choice of leak testing method is crucial. While air leak testing is common due to its lower operational costs, other options like helium mass spectrometry may be used for more precise detection, despite being a more complex, costly approach. Ensuring the right balance between cost, accuracy, and operational feasibility is vital for effective leak testing.
Benefits of In-Line Testing
Manufacturers that use in-line testing can better maintain product integrity throughout production. Integrating testing at various stages of assembly ensures defects are identified and resolved quickly, preventing faulty components from progressing down the line, where they become more and more expensive mistakes. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of producing defective components or products, thereby reducing the likelihood of costly recalls and warranty claims. By catching issues as they arise, manufacturers can enhance overall production efficiency.
When to Use End-of-Line Testing
At the final stages of production, end-of-line testing is essential, particularly for complex and high-value products like battery packs. This type of testing must be used as the last checkpoint to ensure the product is commercially viable and meets all industry standards before it is shipped to customers. It is especially critical in industries where regulatory requirements are stringent or evolving rapidly, such as battery production. By conducting thorough end-of-line testing, manufacturers can verify their product performs as expected under various conditions.
Most importantly, end-of-line testing helps prevent recalls. By identifying and addressing defects at the end of production, manufacturing companies can avoid significant costs and tarnished reputations. This testing provides a final assurance that all components and systems function correctly. Additionally, end-of-line testing can provide valuable feedback to improve earlier stages of production, further enhancing product quality and reducing the likelihood of future recalls.
Even in a product’s first few years of development, leaders need direct feedback on product quality under a variety of conditions. This ensures the final product is robust and reliable for consumer use. Comprehensive testing throughout the production process is critical to minimize warranty and recall penalties. By implementing in-line testing, companies can validate each value-added step, catching defects early and preventing expensive scrap and recalls. In-line testing helps maintain quality standards by identifying any complications as they happen, optimizing production costs and maximizing OEE. Finally, end-of-line testing is the last checkpoint to ensure products meet industry standards or regulations and are commercially viable before leaving the floor.
A comprehensive testing lab that validates manufacturing processes, like the ATS Industrial Automation Test Division, can provide cycle-time-appropriate solutions for electrical tests, leak tests, and more. A strong automation partner can also help manufacturers solve critical process challenges such as dispensing and welding issues—providing even more insights to mitigate the risks of potential recalls or penalties. Contact us to learn more today.
Every testing project is unique. Allow us to listen to your challenges and share how automation can launch your project on time.

Patrick Tabis
Applications Group Lead
ATS Industrial Automation
Patrick helps companies across numerous industries with planning and deploying automation projects on a global scale. Patrick works with customers to optimize the technical design of production lines to drive operational efficiency.